Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy: How they can Effectively Treat Orthopedic Injuries
Many people have been able to gain the benefits of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy for their orthopedic injuries and conditions. Medical professionals may combine PRP and stem cell therapy to boost treatment success. PRP is a regenerative medicine that can harness the ability of the body to heal itself and amplify the natural growth factors that the body uses for healing tissue.
Plasma and Platelets
To understand how PRP therapy works, it is important to understand platelets vs plasma. Plasma refers to the liquid part of whole blood. It consists of water and proteins and offers a medium for red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells to circulate through the body. Platelets are blood cells that cause blood clots and other growth healing functions.
How PRP Therapy Works
Platelet-rich plasma therapy makes use of injections of a concentration of a patient’s own platelets to speed up the healing of injured ligaments, tendons, joints, and muscles. These injections are prepared by taking one to a few tubes of the patient’s blood and running it through a centrifuge to concentrate the platelets. The activated platelets are injected directly in the patient’s injured or diseased body tissue, releasing growth factors that stimulate and increase the number of reparative cells produced by the body.
PRP therapy has been found to dramatically improve the healing of shoulder pain due to rotator cuff tears or Achilles tendon ruptures. Also, it has been shown to improve function and decrease pain in those with tendonitis. The therapy can minimize the need for anti-inflammatory medications or stronger medications such as opioids.
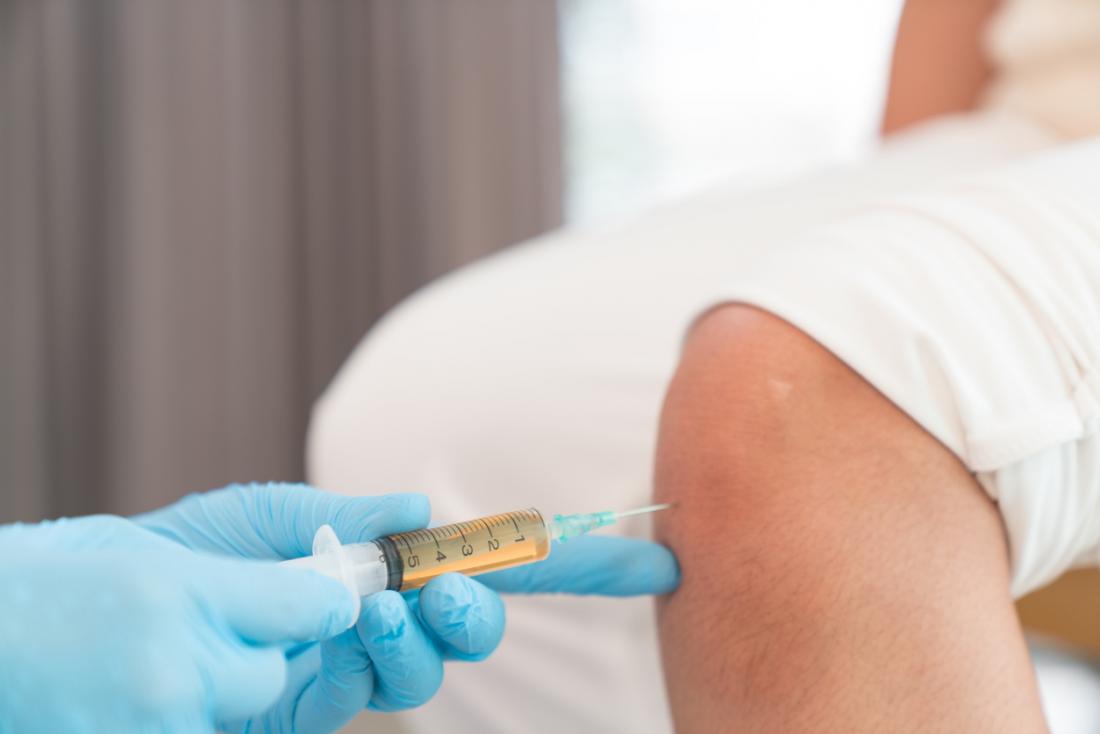
Combining stems cells with Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy
Stem cells and PRP therapy can be combined to accelerate tissue regeneration in advanced degeneration. PRP therapy can increase stem cells and guide them in healing. Thus, the platelets are already attuned to offer a healing environment. In some studies, results confirmed that PRP improves MSC stem cell proliferation and suggested that platelets tell the stem cells what to do. The platelets secret various proteins that regulate different inflammatory responses.
Stem cells can repair cartilage and bone damage. They can change or differentiate themselves into the raw material to rebuild bone and soft tissue. When these cells are injected into a damaged area, they signal the native healing and inflammatory cells into the joint and begin the rebuilding process of the immune system. The blood plasma cells receive these signals and send back confirmation signals.

Comments are closed.